Manual Rev.: 1.1
Revision Date: July 30, 2021
Part Number: 50M-00040-1010
Preface
Copyright
Copyright © 2021 ADLINK Technology, Inc. This document contains proprietary information protected by copyright. All rights are reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced by any mechanical, electronic, or other means in any form without prior written permission of the manufacturer.
Disclaimer
The information in this document is subject to change without prior notice in order to improve reliability, design, and function and does not represent a commitment on the part of the manufacturer. In no event will the manufacturer be liable for direct, indirect, special, incidental, or consequential damages arising out of the use or inability to use the product or documentation, even if advised of the possibility of such damages.
Trademarks
Product names mentioned herein are used for identification purposes only and may be trademarks and/or registered trademarks of their respective companies.
Revision History
| Revision | Description | Date |
|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | Initial release | 2020-10-07 |
| 1.1 | Release for EVA SDK R3.5 | 2021-07-30 |
¶ 1 Introduction
This chapter describes the installation of the following software.
- GStreamer, Gstreamer RTSP Plugin and GStreamer Python Plugin
- NIVIDA® DeepStream, NIVIDA® CUDA and NIVIDA® TensorRT
- Intel® OpenVINO
- Intel® Media SDK for GStreamer
- Pylon Software
- Hikrobot Software
- FLIR Software
- ADLINK EVA SDK
The following table lists the specified software versions.
| Item | Version |
|---|---|
| OS | Ubuntu 18.04 64-bit |
| GStreamer | 1.14.5 |
| NVIDIA® CUDA1 | 11.0 |
| NVIDIA® TensorRT™1 | 7.1.3 |
| NVIDIA® DeepStream1 | 5.1 |
| Intel® OpenVINO™2 | 2021.1.110 |
| Media SDK for GStreamer2 | 1.14.5 (in gst-plugins-bad) |
| OpenCV3 | 4.2.0 or higher |
| Python | 3.6 |
| pylon | 6.1.1 |
| Hikrobot MVS | 2.0.0 |
| Flir Spinnaker SDK | 2.0.0.147 |
Notes:
1 If the NVIDIA solution is used for inference, NVIDIA® DeepStream, NVIDIA® CUDA®, and NVIDIA® TensorRT™ must be installed.
2 If the Intel solution is used for inference, Intel® OpenVINO™ must be installed. To use the Media SDK in GStreamer, install Media SDK for GStreamer.
3 OpenCV is required by the ADLINK EVA SDK. If Intel® OpenVINO is not installed on the system, build and install it. Refer to https://docs.opencv.org/4.5.0/d7/d9f/tutorial_linux_install.html for installation information. Refer to https://opencv.org/ for more information.
The following table lists the estimated installation space required when installing the software under Ubuntu 18.04 64-bit. The required installation space includes the install file (.deb, .run, .tgz) package size.
| Software | Required Installation Space |
|---|---|
| GStreamer | 550MB |
| GStreamer Python Plugin | 600MB |
| NVIDIA Driver | 750MB |
| NVIDIA® CUDA | 7.9GB (deb file: 2.3GB) |
| NVIDIA® TensorRT™ | 7.3GB (deb file: 1.3GB) |
| librdkafka | 150MB |
| NVIDIA® DeepStream | 800MB (tar file: 500MB) |
| Intel® OpenVINO™ | 1.7GB (tgz file: 500MB) |
| Media SDK for GStreamer | 300MB |
| Pylon | 430MB (deb file: 90MB) |
| Hikrobot MVS | 400MB (zip file: 132MB) |
| Flir Spinnaker SDK | 300MB (gz file: 72MB) |
¶ 2 Installing GStreamer on Ubuntu
The recommended installation configuration requires installing Gstreamer 1.14.5 on Ubuntu 18.04.
¶ 2.1 Install GStreamer on Ubuntu
| $ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install git libgstreamer1.0-0 gstreamer1.0-plugins-base gstreamer1.0-plugins-good gstreamer1.0-plugins-bad gstreamer1.0-plugins-ugly gstreamer1.0-libav gstreamer1.0-doc gstreamer1.0-tools gstreamer1.0-x gstreamer1.0-alsa gstreamer1.0-gl gstreamer1.0-gtk3 gstreamer1.0-qt5 gstreamer1.0-pulseaudio |
Reference: https://gstreamer.freedesktop.org/documentation/installing/on-linux.html?gi-language=c
¶ 2.2 Check the GStreamer Installation
| $ gst-launch-1.0 videotestsrc ! videoconvert ! autovideosink |
After executing the command, a window with an animated video pattern should display on-screen. Use CTRL+C in the terminal to stop the program.
¶ 2.3 Install RTSP Plugin for GStreamer (Optional)
If the data will be sent over an RTSP server, the system must have the RTSP plugin installed with the following command for GStreaming.
| $ sudo apt install gstreamer1.0-rtsp |
Use the following command to verify the installation.
| $ gst-inspect-1.0 rtspclientsink |

¶ 3 Installing the GStreamer Python Plugin
GStreamer is built on the GLib and GObject portable libraries which are compatible with Python. Gstreamer can be used in two ways: by writing GStreamer applications, or by writing GStreamer Python elements that can be scanned by the GStreamer Python plugin loader and registered as a plugin in GObject. The following sections describe how to install the GStreamer Python plugin.
¶ 3.1 Install the Required Packages
| $ sudo apt-get install python3-pip python-gi-dev python3-gst-1.0 |
If your platform is using Python 2.7, change the python3-gst-1.0 package to python-gst-1.0.
¶ 3.2 Install the GStreamer Python Plugin Loader
Currently, the Debian GStreamer Python package includes GObject Introspection files but does not include the GStreamer Python plugin loader, requiring the use of a GStreamer Python application.
GStreamer Python plugins cannot be scanned and registered in applications like gst-launch-1.0 or gst-inspect-1.0, so a GStreamer Python plugin loader must be built.
1. Clone the GStreamer gst-python repository
| $ git clone -b 1.14 https://github.com/GStreamer/gst-python.git |
2. Install the build tool
| $ pip3 install --user meson ninja |
When using Python 2.7, call pip instead of pip3.
3. Add the Python binary search path
| $ export PATH=~/.local/bin:$PATH |
If installing the meson package via apt installs an old version of meson, make sure the meson binary installed by pip3 can be found by first specifying where to access the Python binary.
4. Build and install gst-python
| $ cd gst-python $ meson _build -Dprefix=$PWD/local $ ninja -C _build install |
At this point, it is important not to overwrite the previously installed GStreamer Python files which can possibly have a negative impact on the system. Instead, install GStreamer Python to a local folder and then copy only the required files.
5. Copy GStreamer Python plugin loader
The previous build steps generated two kinds of files, GObject introspection files and the GStreamer Python plugin loader in the following directory structure.
Gst-python install directory structure
|
local |
Copy libgstpython.so to the GStreamer system plugin folder, or other plugin folders as necessary.
Copy the required library
| $ sudo cp local/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/gstreamer-1.0/libgstpython.so /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/gstreamer-1.0 |
6. Install the required Python packages
| $ pip3 install --upgrade pip $ sudo pip3 install scikit-build cmake boto3 $ sudo pip3 install opencv-python numpy |
Notes:
- If the CPU is an Intel® Atom™ series processor, installation of opencv-python will take about 1 to 1.5 hours. Do not interrupt the installation process.
- The following message can be ignored when executing pip with sudo.
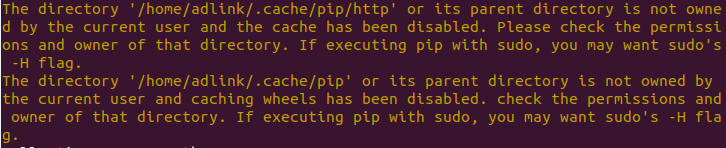
7. Check for installed Python plugins
| $ cd .. # Stay in gst-python will cause python local wrong gi module in gst-python folder $ GST_DEBUG=pyplugin:7 gst-inspect-1.0 python |
If the Python plugins are found, the installation has been successful.
¶ 4 Installation Process for NVIDIA Solution (Optional)
The ADLINK EVA SDK also supports the NVIDIA inference solution based on your specific system configuration requirements.
For ADLINK EVA SDK with the NVIDIA solution, the following components must be installed on Ubuntu 18.04:
- GStreamer 1.14.x
- NVIDIA Driver 450.51 or higher
- CUDA 11.0
- TensorRT 7.1.3
- DeepStream 5.1 (optional)
This chapter will describe the installation and uninstallation steps provided on the NVIDIA official website.
If you are not using an NVIDIA inference solution, this chapter can be skipped.
¶ 4.1 Uninstall Non-specified Version
This section describes how to unistall a non-specified version of the NVIDIA solution software. After the components have been removed, you must reboot the system.
¶ 4.1.1 Remove DeepStream
Check the DeepStream Version
| $ cd spinnaker-<version> $ deepstream-app --version-all |
DeepStream 3.0 or earlier version removal:
| $ sudo rm -rf /usr/local/deepstream /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/gstreamer-1.0/libgstnv* /usr/bin/deepstream* /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/gstreamer-1.0/libnvdsgst* /opt/nvidia/deepstream/deepstream* /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/gstreamer-1.0/deepstream* $ sudo rm -rf /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libv41/plugins/libcuvidv4l2_plugin.so |
DeepStream 4.0 or later version removal:
- Open the uninstall.sh file in /opt/nvidia/deepstream/deepstream/
- Set PREV_DS_VER as the version number (e.g: 4.0)
- Run the following command script
| $ sudo ./uninstall.sh |
¶ 4.1.2 Remove TensorRT
Check the TensorRT version
| $ dpkg -l | grep nvinfer |
Remove TensorRT
| $ sudo apt-get --purge remove "*tensorrt*" $ sudo apt-get --purge remove "libnvinfer*" $ sudo apt-get autoremove |
Reference: https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/tensorrt/install-guide/index.html#uninstalling.
¶ 4.1.3 Remove CUDA
Check the CUDA version
| $ /usr/local/cuda/bin/nvcc --version |
Remove the CUDA Toolkit
| $ sudo apt-get --purge remove "*cublas*" "*cufft*" "*curand*" "*cusolver*" "*cusparse*" "*npp*" "*nvjpeg*" "cuda*" "nsight*" $ sudo apt-get autoremove |
Notes:
- If using a runfile for installation, refer to https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cuda-installation-guide-linux/index.html#handle-uninstallation
- Reference: https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cuda-installation-guide-linux/index.html#removing-cuda-tk-and-driver
¶ 4.1.4 Remove NVIDIA Drivers
Check the driver
| $ nvidia-smi |
Remove NVIDIA Drivers
| $ sudo apt-get --purge remove "nvidia-driver*" $ sudo apt-get autoremove $ sudo reboot |
¶ 4.2 Installing NVIDIA Drivers
Before installing the NVIDIA graphics driver, use the “Software Updater” to install updated software first.
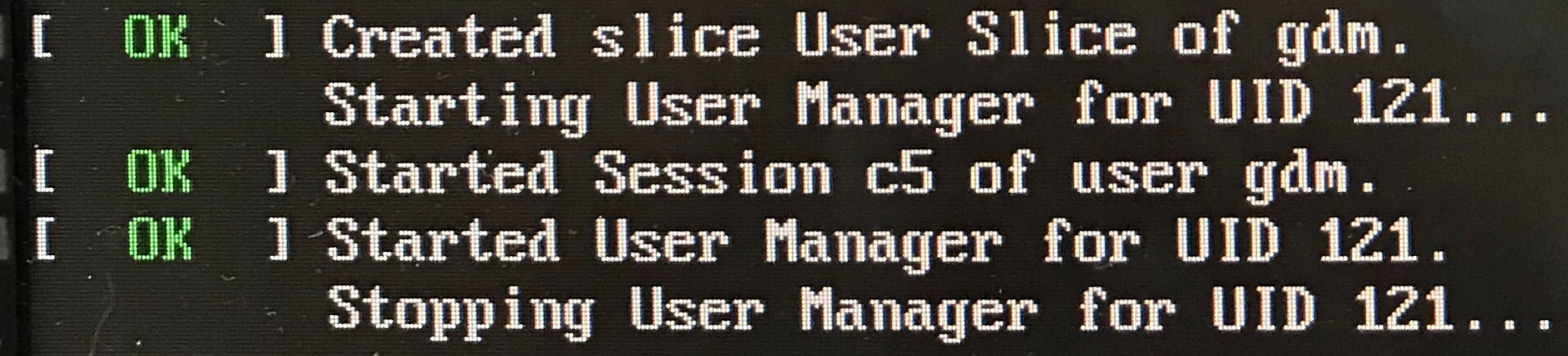
If the system software is not updated, after installing the NVIDIA driver and rebooting, the system can hang with the following message: “Stopping User Manager for UID 121”.
Insert the NVIDIA graphics card and follow the steps below to install the drivers.
1. Add the graphics-drivers repository to advanced package tool (apt)
| $ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:graphics-drivers/ppa $ sudo apt update |
2. Check the NVIDIA Driver list
| $ ubuntu-drivers devices |
In this example, the system must have an NVIDIA device with a recommend driver version of 450 or later.
| $ ubuntu-drivers devices == /sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:1c.0/0000:02:00.0/0000:03:01.0/0000:04:00.0 == modalias : pci:v000010DEd00001CFAsv0000144Asd00004200bc03sc00i00 vendor : NVIDIA Corporation driver : nvidia-driver-450 - distro non-free driver : nvidia-driver-460 - third-party free recommended driver : nvidia-driver-450-server - distro non-free driver : xserver-xorg-video-nouveau - distro free builtin |
3. Install the NVIDIA Driver
| $ sudo apt install nvidia-driver-450 $ sudo reboot |
4. Check the driver
| $ nvidia-smi |
In this example, the system installed driver version is 450 and supports CUDA driver version 11.
| $ nvidia-smi Wed Jan 27 14:32:01 2021 +-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | NVIDIA-SMI 450.102.04 Driver Version: 450.102.04 CUDA Version: 11.0 | |-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+ | GPU Name Persistence-M| Bus-Id Disp.A | Volatile Uncorr. ECC | | Fan Temp Perf Pwr:Usage/Cap| Memory-Usage | GPU-Util Compute M. | | | | MIG M. | |===============================+======================+======================| | 0 Quadro P2000 Off | 00000000:04:00.0 On | N/A | | N/A 39C P0 N/A / N/A | 301MiB / 4037MiB | 0% Default | | | | N/A | +-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Processes: | | GPU GI CI PID Type Process name GPU Memory | | ID ID Usage | |=============================================================================| | 0 N/A N/A 992 G /usr/lib/xorg/Xorg 220MiB | | 0 N/A N/A 1223 G /usr/bin/gnome-shell 77MiB |
|
¶ 4.3 Installing CUDA Toolkit 11
Download the CUDA Toolkit 11.0 original archive from https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-11.0-download-archive?target_os=Linux&target_arch=x86_64&target_distro=Ubuntu&target_version=1804&target_type=deblocal
The target platform must conform to the following requirements:
- Operation System: Linux
- Architecture: x86_64
- Distribution: Ubuntu
- Version: 18.04
- Installer Type: deb(local)
Run the following installation commands.
| $ wget https://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/repos/ubuntu1804/x86_64/cuda-ubuntu1804.pin $ sudo mv cuda-ubuntu1804.pin /etc/apt/preferences.d/cuda-repository-pin-600 $ wget http://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/11.0.2/local_installers/cuda-repo-ubuntu1804-11-0-local_11.0.2-450.51.05-1_amd64.deb $ sudo dpkg -i cuda-repo-ubuntu1804-11-0-local_11.0.2-450.51.05-1_amd64.deb $ sudo apt-key add /var/cuda-repo-ubuntu1804-11-0-local/7fa2af80.pub $ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get -y install cuda |
¶ 4.4 Installing TensorRT 7.1.3
Download TensorRT 7.1.3 for Linux from https://developer.nvidia.com/compute/machine-learning/tensorrt/secure/7.1/local_repo/nv-tensorrt-repo-ubuntu1804-cuda11.0-trt7.1.3.4-ga-20200617_1-1_amd64.deb
Select Log in or Join now.
After downloading, install TensorRT from the debian local repository package with the following commands:
| $ sudo dpkg -i nv-tensorrt-repo-ubuntu1804-cuda11.0-trt7.1.3.4-ga-20200617_1-1_amd64.deb $ sudo apt-key add /var/nv-tensorrt-repo-cuda11.0-trt7.1.3.4-ga-20200617/7fa2af80.pub $ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install tensorrt |
Refer to the Debian installation online document for more information at https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/tensorrt/archives/tensorrt-713/install-guide/index.html#installing-debian
¶ 4.5 Installing DeepStream 5.1 (Optional)
If you are not using a DeepStream SDK, this section can be skipped.
The NVIDIA DeepStream SDK first requires installation of the following components:
- GStreamer
- NVIDIA Driver
- CUDA
- TensorRT
1. Install packages
Enter the following command to install the necessary packages before installing the DeepStream SDK:
| $ sudo apt install libssl1.0.0 libgstreamer1.0-0 gstreamer1.0-tools gstreamer1.0-plugins-good gstreamer1.0-plugins-bad gstreamer1.0-plugins-ugly gstreamer1.0-libav libgstrtspserver-1.0-0 libjansson4 |
2. Install librdkafka
librdkafka enables the Kafka protocol adaptor for message brokering.
Clone the librdkafka repository from GitHub
| $ git clone https://github.com/edenhill/librdkafka.git |
Configure and build the library
| $ cd librdkafka $ git reset --hard 7101c2310341ab3f4675fc565f64f0967e135a6a $ ./configure $ make $ sudo make install |
Copy the generated libraries to the DeepStream directory
| $ sudo mkdir -p /opt/nvidia/deepstream/deepstream-5.1/lib $ sudo cp /usr/local/lib/librdkafka* /opt/nvidia/deepstream/deepstream-5.1/lib |
3. Install the DeepStream SDK 5.1
Download the DeepStream 5.1 dGPU tar package from https://developer.nvidia.com/deepstream-sdk-v510-x86-64tbz2.
Navigate to the location of the downloaded DeepStream package to extract and install the DeepStream SDK.
| $ sudo tar -xvf deepstream_sdk_v5.1.0_x86_64.tbz2 -C / $ cd /opt/nvidia/deepstream/deepstream-5.1/ $ sudo ./install.sh $ sudo ldconfig |
Note:
NVIDIA provides three methods for installing the DeepStream SDK. The tar package MUST be used for installation. Attempting to use the Debian package or apt-server to install, will result in compatibility issues.
¶ 4.5.1 Verify DeepStream
After installing DeepStream, follow these steps to verify the installation.
1. Check version information
| $ deepstream-app --version-all |
2. Check the plugin in GStreamer
| $ gst-inspect-1.0 | grep nv |
3. Verify the plugin via gst-launch
| gst-launch-1.0 videotestsrc num-buffers=1000 ! videoconvert ! "video/x-raw,format=(string)I420" ! nvvideoconvert ! nvv4l2h264enc ! h264parse ! matroskamux ! filesink location=videotestsrc.mkv |
The following is an example of a properly installed package.
| $ gst-inspect-1.0 | grep nv nvdsgst_jpegdec: nvjpegdec: JPEG image decoder $ deepstream-app --version-all deepstream-app version 5.1.0 $ gst-launch-1.0 videotestsrc num-buffers=1000 ! videoconvert ! "video/x-raw,format=(string)I420" ! nvvideoconvert ! nvv4l2h264enc ! h264parse ! matroskamux ! filesink location=videotestsrc.mkv Setting pipeline to PAUSED ... |
Note:
When running a GStreamer command or EVA IDE, the following warning messaging will display.
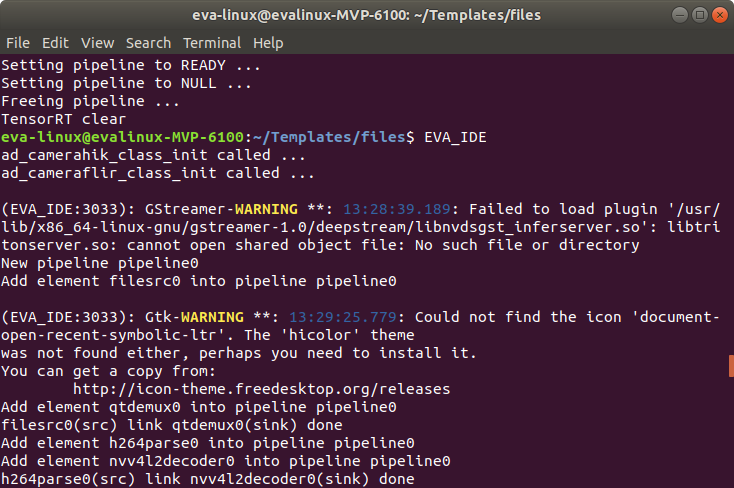
This is a harmless warning indicating that the DeepStream’s nvinferserver plugin cannot be used since “Triton Inference Server” is not installed on x86(dGPU) platforms.
Refer to NVIDIA troubleshooting for other solutions. https://docs.nvidia.com/metropolis/deepstream/dev-guide/text/DS_troubleshooting.html#errors-occur-when-deepstream-app-fails-to-load-plugin-gst-nvinferserver-on-dgpu-only
¶ 4.6 Installing ONNX Runtime
After installing the CUDA Toolkit, run the following command to install the ONNX Runtime packages.
| > pip3 install pillow > pip3 install onnxruntime-gpu==1.8.0 |

Reference: https://www.onnxruntime.ai/
¶ 5 Installation Process for Intel Solution (Optional)
The ADLINK EVA SDK also supports the Intel OpenVINO inference solution based on your specific system configuration requirements.
For ADLINK EVA SDK with the Intel solution, the following components must be installed on Ubuntu 18.04:
- OpenVINO 2021.1.110
- Intel Media SDK plugin for GStreamer (optional)
If you are not using the Intel® Distribution of OpenVINO™ toolkit, this chapter can be skipped.
¶ 5.1 Uninstall Non-specified Version
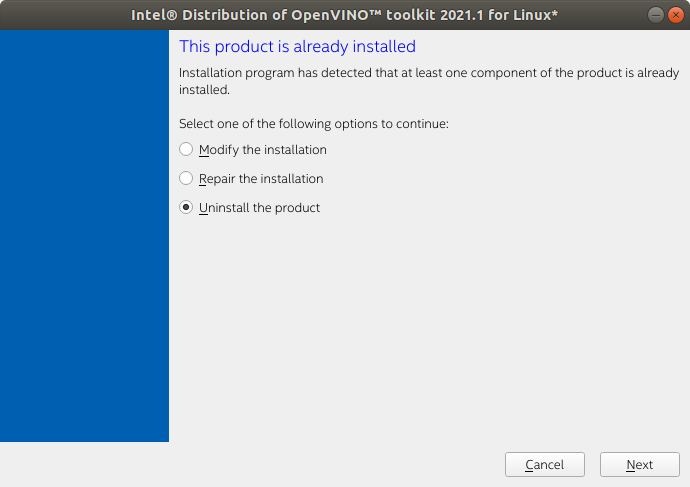
If the system has a non-specified version of OpenVINO, use the OpenVINO toolkit installation package to uninstall it.
| $ cd [OpenVINO toolkit installation package folder]
##Please move the path according to the actual directory location $ sudo ./install_GUI.sh |
Choose Uninstall the product and follow the instructions on the screen to uninstall.
¶ 5.2 Installing the OpenVINO Toolkit
The Intel® Distribution of OpenVINO™ toolkit is a comprehensive toolkit for quickly developing applications and solutions that solve a variety of tasks including emulation of human vision, automatic speech recognition, natural language processing, recommendation systems, and many others.
The OpenVINO™ toolkit for Linux:
- Enables CNN-based deep learning inference on the edge
- Supports heterogeneous execution across Intel® CPU, Intel® Integrated Graphics, Intel® Movidius™ Neural Compute Stick, Intel® Neural Compute Stick 2, and Intel® Vision Accelerator Design with Intel® Movidius™ VPUs
- Speeds time-to-market via an easy-to-use library of computer vision functions and pre-optimized kernels
- Includes optimized calls for computer vision standards including OpenCV* and OpenCL™
For more details, refer tohttps://docs.openvinotoolkit.org/2021.1/openvino_docs_install_guides_installing_openvino_linux.html.
.
1. Install the Intel® Distribution of OpenVINO™ Toolkit Core Components
If you have a previous version of the Intel Distribution of OpenVINO toolkit installed, and the following directories exist, rename or delete them:
~/inference_engine_samples_build
~/openvino_models
Download the Intel® Distribution of OpenVINO™ toolkit package file from Intel® Distribution of OpenVINO™ toolkit for Linux* (https://software.intel.com/en-us/openvino-toolkit/choose-download)
Select the Intel® Distribution of OpenVINO™ toolkit for Linux package to download according to the following:
- Operation System: Linux
- Distribution: Web and Local Install
- Installer Type: Local
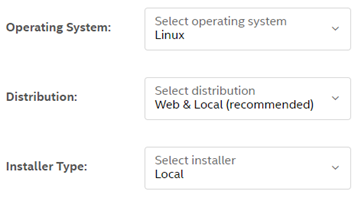
Click Register & Download, choose Linux and complete the registration form.
On the Intel® Distribution of OpenVINO™ toolkit for Windows website, choose version ‘2021 1’ and click Full Package.
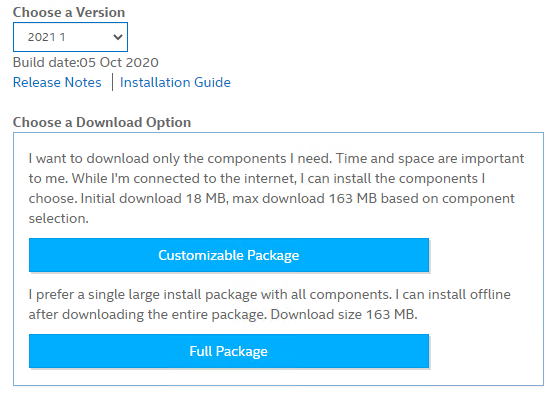
After downloading, install the OpenVino toolkit via by entering the following commands to start the installer GUI.
| $ cd ~/Downloads/ $ tar -xvzf l_openvino_toolkit_p_2021.1.110.tgz $ cd l_openvino_toolkit_p_2021.1.110 $ sudo ./install_GUI.sh |
1. Follow the instructions on your screen. Watch for informational messages such as the following in case you must complete additional steps:

2. Click Customize…
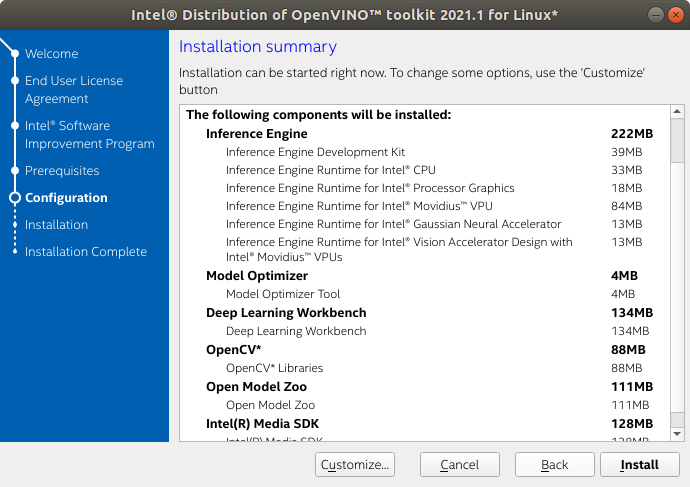
3. DO NOT modify the installation location. Click Next.
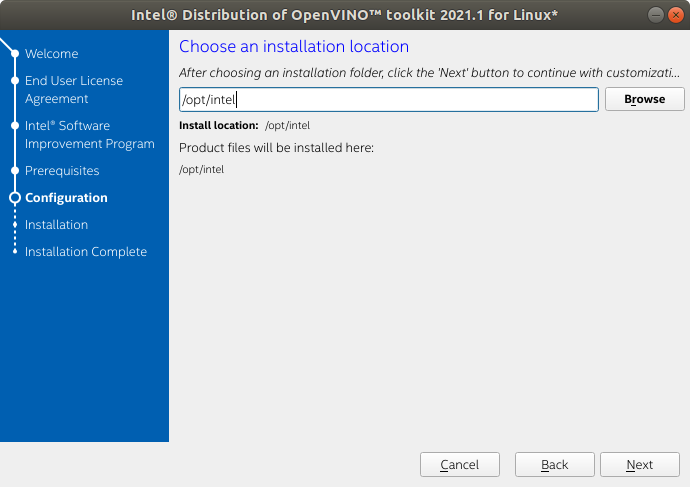
4. Disable DL Streamer and then click Next.
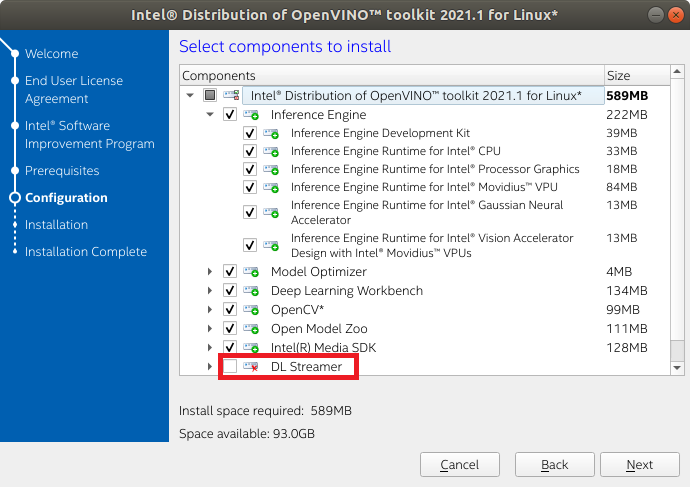
Note:
If the DL streamer is installed, GStreamer will display warning messages after installing OpenVINO and the msdk plugin will not work after installing Intel Media SDK for GStreamer.
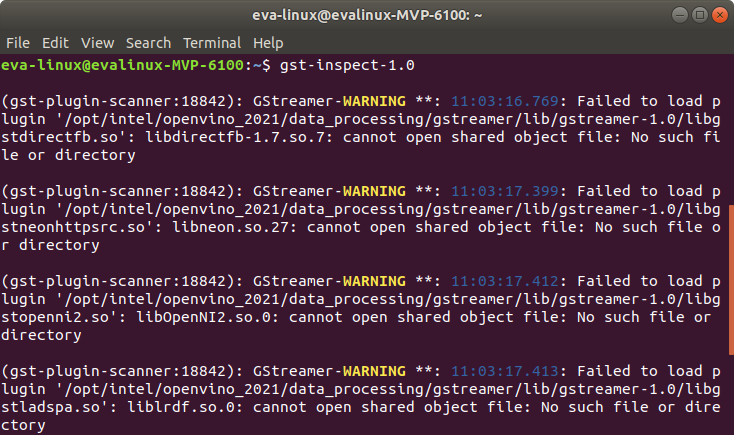
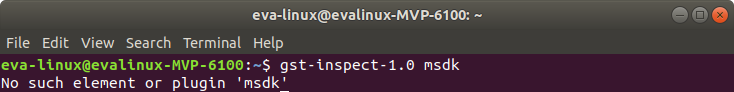
5. Click Install to start installing.

Note:
The Intel® Media SDK component is always installed in the /opt/intel/mediasdk directory regardless of the OpenVINO installation path chosen.
6. A Complete screen indicates that the core components have been installed:

2. Install External Software Dependencies
These dependencies are required for:
- Intel-optimized build of OpenCV library
- Deep Learning Inference Engine
- Deep Learning Model Optimizer tools
Install the external software dependencies
| $ cd /opt/intel/openvino_2021/install_dependencies $ sudo -E ./install_openvino_dependencies.sh |
3. Set the Environment Variables
Set environment variables for OpenVino
| $ source /opt/intel/openvino_2021/bin/setupvars.sh |
Optional: The OpenVINO environment variables are removed when you close the shell. As an option, you can permanently set the environment variables as follows:
- Open the .bashrc file
| $ gedit ~/.bashrc |
- Add this line to the end of the file
| source /opt/intel/openvino_2021/bin/setupvars.sh |
- To test your change, open a new terminal. You should see [setupvars.sh] OpenVINO environment initialized.
4. Optional Steps for Intel® Processor Graphics (GPU)
The steps in this section are required only if you want to enable the toolkit components to use processor graphics (GPU) on your system.
Install OCL driver
| $ cd /opt/intel/openvino_2021/install_dependencies/ $ sudo -E su $ ./install_NEO_OCL_driver.sh |
You may see the following command line output:
- Add OpenCL user to video group
- Run script to install the 4.14 kernel script
Ignore those suggestions and continue.
5. Optional Steps for Intel® Movidius™ Neural Compute Stick and Intel® Neural Compute Stick 2
These steps are only required if you want to perform inference on Intel® Movidius™ NCS powered by the Intel® Movidius™ Myriad™ 2 VPU or Intel® Neural Compute Stick 2 powered by the Intel® Movidius™ Myriad™ X VPU.
Add the current Linux user to the users group
| $ sudo usermod -a -G users "$(whoami)" |
Log out and log in for it to take effect.
To perform inference on Intel® Movidius™ Neural Compute Stick and Intel® Neural Compute Stick 2, install the USB rules as follows.
| $ sudo cp /opt/intel/openvino_2021/inference_engine/external/97-myriad-usbboot.rules /etc/udev/rules.d/ $ sudo udevadm control --reload-rules $ sudo udevadm trigger $ sudo ldconfig |
Note:
You may need to reboot your machine for this to take effect.
¶ 5.3 Installing the Intel Media SDK Plugin for Gstreamer (Optional)
If you would like to use Media SDK plugin in GStreamer, install OpenVinoTM first. It will include Intel Media SDK and the related libraries such as VAAPI, LibVA, and gmmlib.
The Intel Media SDK plugin source code is in gst-plugins-bad module, but as of Aug. 23, 2019, the GStreamer package installed via apt-get does not contain the msdk plugin, so it must be built and installed.
For more details, refer to https://github.com/Intel-Media-SDK/MediaSDK/wiki/Build-and-use-GStreamer-with-MediaSDK.
1. Prepare the environment and dependencies
Install OpenVino and export environment variables.
- export LIBVA_DRIVER_NAME=iHD
- export LIBVA_DRIVERS_PATH=/path/to/iHD_driver
- export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/path/to/msdk/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
- export PKG_CONFIG_PATH=/path/to/msdk/lib/pkgconfig:$ PKG_CONFIG_PATH
Notes:
- /path/to/iHD_driver: use the MediaSDK iHD driver path. If you install OpenVino for Media SDK, the path should be /opt/intel/mediasdk/lib64.
- /path/to/msdk/lib: use the MediaSDK library's path. If you install OpenVino for Media SDK, the path should be /opt/intel/mediasdk/lib64.
- You may need to set the environment for the system permanently.
- Open the .bashrc file in your home directory, for example:
$ gedit ~/.bashrc - Add export environment variables to the last line of the file, for example:
- export LIBVA_DRIVER_NAME=iHD
- export LIBVA_DRIVERS_PATH=/opt/intel/mediasdk/lib64
- export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/opt/intel/mediasdk/lib64:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
- export PKG_CONFIG_PATH=/opt/intel/mediasdk/lib64/pkgconfig:$PKG_CONFIG_PATH
- Save the .bashrc file.
- Restart your terminal.
- Open the .bashrc file in your home directory, for example:
2. Download and build the source code
Because GStreamer 1.14.5 is required, download the 1.14 branch from gst-plugins-bad git.
Download the source code
| $ git clone -b 1.14 https://gitlab.freedesktop.org/gstreamer/gst-plugins-bad.git |
Before building, install the following package
| $ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install gtk-doc-tools libgstreamer1.0-dev libgstreamer-plugins-base1.0-dev libgudev-1.0-dev |
Build and install the source code
| $ cd gst-plugins-bad $ ./autogen.sh --prefix=$PWD/local $ make -j $(nproc) && make install $ sudo cp $PWD/local/lib/gstreamer-1.0/libgstmsdk.so /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/gstreamer-1.0 |
Note:
Check the configuration for included MSDK plugins.
- After executing autogen.sh,the configuration log must contain:
- configure: *** Plug-ins with dependencies that will be built: should include msdk.
- configure: *** checking feature: Intel MediaSDK ***
configure: *** for plug-ins: msdk ***
checking for G_UDEV... yes
checking for LIBMFX... yes
checking for LIBVA_DRM... yes
configure: *** These plugins will be built: msdk
- If msdk is not included, check the environment variable settings and that the libraries above exist. If a library does not exist, install it. For example, checking for G_UDEV... no, install libgudev-1.0.dev.
Check for the msdk plugin
| $ gst-inspect-1.0 | grep msdk |
The following is an example of the installed package.
| $ gst-inspect-1.0 | grep msdk msdk: msdkh264dec: Intel MSDK H264 decoder |
¶ 6 Installing Pylon Software (Optional)
If you are not using a Basler camera, you can skip this chapter.
¶ 6.1 Uninstall Non-specified Version
If the system has a non-specified version of the Pylon software, uninstall it.
If the installer is installed via deb, refer to the following command to remove pylon.
| $ sudo apt-get remove pylon |
¶ 6.2 Install pylon Software
If Basler cameras are used, the Pylon Software must be installed.
Download the pylon camera software from the Basler website at: https://www.baslerweb.com/en/sales-support/downloads/software-downloads/
The recommended software versions are:
- Software Category: pylon Software
- Version: 6.1.1
- Operating System: Linux x86-64 bit
Also, you can use the link https://www.baslerweb.com/en/sales-support/downloads/software-downloads/#type=pylonsoftware;language=all;version=6.1.1;os=linuxx8664bit
Download the Debian Installer Package and double-click the file.
Click Install to begin installing pylon.
Optionally, you can use the following install command.
| $ sudo dpkg -i pylon_6.1.1.19861-deb0_amd64.deb |
After the installation is completed, set the pylon library path environment variable with LD_LIBRARY_PATH.
For example, if the pylon library path is /opt/pylon/lib, execute the following command:
| $ export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/opt/pylon/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH |
Note:
You may need to set the environment for the system permanently.
- Open the .bashrc file in your home directory, for example:
$ gedit ~/.bashrc - Add export environment variables to the last line of the file, for example:
- export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/opt/pylon/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
- Save the .bashrc file.
- Restart your terminal.
Verify the Basler's USB3/GigE Vision cameras with pylon
- After installing pylon, run the pylonviewer tool to test the camera.
- The file should be at /opt/pylon/bin.
- Refer to the following Basler document on using the pylonviewer: https://docs.baslerweb.com/overview-of-the-pylon-viewer.html
¶ 7 Installing Hikrobot Software (Optional)
If you are not using a Hikrobot camera, you can skip this chapter.
If Hikrobot cameras are used, the Hikrobot MVS Software must be installed.
Download the Hikrobot installer from: https://en.hikrobotics.com/machinevision/service/download?module=0
The recommended software versions are:
- Version: Machine Vision Industrial Camera SDK 2.0.0 (Linux X86)
- Operating System: Linux 64-bit
Run the following commands and then follow the screen instructions to install.
| $ unzip "MVS_V2.0.0_200312(Linux X86).zip" $ cd "MVS_V2.0.0_200312(Linux X86)" $ tar xvfz MVS-2.0.0_x86_64_20200312.tar.gz $ cd MVS-2.0.0_x86_64_20200312 $ sudo ./setup.sh |
After installing, connect the camera and run the MVS software to verify that it works. The file should be at /opt/MVS/bin.
Note:
The above installation steps are for reference only. For more specific installation instructions, refer to the official documentation, or contact Hikrobot at https://en.hikrobotics.com/contactus.
¶ 8 Installing FLIR Software (Optional)
This chapter covers the installation of required software for use with FLIR cameras.
If you are not using a FLIR camera, this chapter can be skipped.
¶ 8.1 Uninstall Non-specified Version
If the system has a non-specified version of the FLIR Spinnaker software, uninstall it.
Run the uninstall script with the Spinnaker installation package.
| $ cd spinnaker- $ sudo ./remove_spinnaker.sh |
¶ 8.2 Install FLIR Spinnaker Software
If FLIR cameras are used, the FLIR Spinnaker Software Suite for Windows must be installed.
Download the FLIR Spinnaker installer from: https://www.flir.asia/products/spinnaker-sdk/
The recommended software versions are:
- Version: spinnaker-2.0.0.147-Ubuntu18.04-amd64
- Operating System: Linux 64 bit
File path: FLIR Support/Spinnaker/archive/2.0.0.147
Run the following commands and then follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation.
| $ tar xvfz spinnaker-2.0.0.147-Ubuntu18.04-amd64-pkg.tar.gz $ cd spinnaker-2.0.0.147-amd64 $ sudo ./install_spinnaker.sh $ sudo reboot |
Note:
During installation, you MUST enter a “username” to add a new member.
For example, enter ‘adlink’ for the user name.

After installation, connect the camera and run the following command to verify that it works.
| $ spinview |
Note:
For more information, refer to https://www.flir.com/support-center/iis/machine-vision/application-note/using-spinnaker-on-arm-and-embedded-systems/
If you have any questions, go to https://www.flir.com/.
¶ 9 Installing the ADLINK EVA SDK
¶ 9.1 Remove Previous ADLINK EVA SDK Versions
If you have a previously installed version of the ADLINK EVA SDK, remove it with the following command:
| $ sudo /opt/adlink/eva/uninstall.sh |
If the install path has been changed, specified the correct path with:
| $ sudo [INSTALL_DIR]/uninstall.sh |
INSTALL_DIR enters the specified path.
Note:
When uninstalling the ADLINK EVA SDK, the folder specified with INSTALL_DIR will be deleted.
¶ 9.2 Install the Required Package for EVA IDE
| $ sudo apt-get install graphviz |
¶ 9.3 Download and Install the ADLINK EVA SDK
Download the ADLINK EVA SDK installation package and copy it to your Linux Ubuntu 18.04 64-bit system.
Change mode and run install package
| $ chmod +x EVA_SERP_xxxx.run $ sudo ./EVA_SERP_xxxx.run |
xxxx is the version and the install path is /opt/adlink/eva.
Select the EVA SDK plugins to be installed.
|
Select GStreamer plugin to install. (Separate with comma, for example, “2,3,4”).
|
For example, to install the TensorRT inference plugin and the Pylon plugin, enter 3,4. To install all plugins, including the OpenVINO inference plugin, TensorRT inference plugin, Pylon plugin, Hik plugin, and Flir plugin, enter 1.
Notes:
- OpenVINO is only supported on Intel platforms.
- TensorRT is only supported on NVIDIA platforms.
- Before installing the EVA SDK, you must ensure the corresponding software packages have been installed. If the plugins are installed but there are no corresponding libraries, when the GStreamer command runs for the first time, it will display messages to warn that the related libraries are missing, and the installed plugins will not work.
Other commands can be used to install the ADLINK EVA SDK.
- Use the -s command option to install all the plugins in silent mode. The install path is /opt/adlink/eva.
| $ sudo ./EVA_SERP_xxxx.run -- -s |
¶ 9.4 Set Environment Variables
Set environment variables for the ADLINK EVA SDK
| $ source /opt/adlink/eva/scripts/setup_eva_envs.sh |
The script will set up the environment variables of the following installed software.
- OpenVINO
- MediaSDK
- Pylon
- ADLINK EVA SDK
If the software has no corresponding libraries, the script will not set up the corresponding environment variables.
Note:
The environment variables are removed when closing the command prompt or terminal.
Safety Instructions
Read and follow all instructions marked on the product and in the documentation before you operate your system. Retain all safety and operating instructions for future use.
- Please read these safety instructions carefully.
- Please keep this User‘s Manual for later reference.
- Read the specifications section of this manual for detailed information on the operating environment of this equipment.
- When installing/mounting or uninstalling/removing equipment, turn off the power and unplug any power cords/cables.
- To avoid electrical shock and/or damage to equipment:
- Keep equipment away from water or liquid sources.
- Keep equipment away from high heat or high humidity.
- Keep equipment properly ventilated (do not block or cover ventilation openings).
- Make sure to use recommended voltage and power source settings.
- Always install and operate equipment near an easily accessible electrical socket-outlet.
- Secure the power cord (do not place any object on/over the power cord).
- Only install/attach and operate equipment on stable surfaces and/or recommended mountings.
- If the equipment will not be used for long periods of time, turn off and unplug the equipment from its power source.
- Never attempt to fix the equipment. Equipment should only be serviced by qualified personnel.
Getting Service
Ask an Expert: http://askanexpert.adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology, Inc.
Address:9F, No.166 Jian Yi Road, Zhonghe District
New Taipei City 235, Taiwan
Tel: +886-2-8226-5877
Fax: +886-2-8226-5717
Email: service@adlinktech.com
Ampro ADLINK Technology, Inc.
Address:5215 Hellyer Avenue, #110, San Jose, CA 95138, USA
Tel: +1-408-360-0200
Toll Free:+1-800-966-5200 (USA only)
Fax: +1-408-360-0222
Email: info@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology (China) Co., Ltd.
Address:300 Fang Chun Rd., Zhangjiang Hi-Tech Park, Pudong New Area
Shanghai, 201203 China
Tel: +86-21-5132-8988
Fax: +86-21-5132-3588
Email: market@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology GmbH
Address:Hans-Thoma-Straße 11
D-68163 Mannheim, Germany
Tel: +49-621-43214-0
Fax: +49-621 43214-30
Email: germany@adlinktech.com
Please visit the Contact page at www.adlinktech.com for information on how to contact the ADLINK regional office nearest you.